
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in a living cell contains the master blueprint for the production of proteins and for the replication of itself. It is the repository for the hereditary information. DNA accomplishes protein production by first providing a pattern for the production of mRNA, a process called transcription. The RNA then contains the information from the DNA to manufacture a protein, a process called translation. Some proteins are structural, but some are control proteins called enzymes. These enzymes are employed in the production of proteins, even copies of themselves, so enzymes are used to make other enzymes. Each protein, including enzymes, is made according to a pattern of nucleotides along a segment of the DNA called a "gene". A single living cell contains thousands of enzymes.
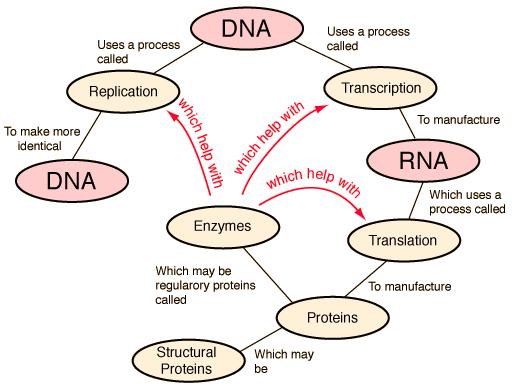
Another way to organized these ideas is in terms of the "central dogma" of molecular biology.
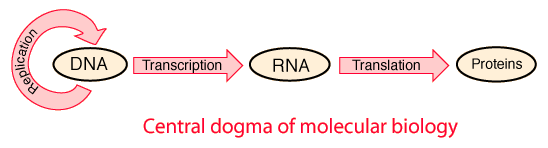
Active graphics.Though a useful organizing structure, the "central dogma" has numerous exceptions. For example, retroviruses use "reverse transcription" to construct DNA from RNA. In general, not every gene gets expressed all the way to the construction of proteins. Some RNAs have other tasks to do, such as the ribosomal RNA and other specifically tasked RNAs with specific tasks in the cell.








